- Emergency Admission : +91-8585035846
- Email :feedback@bppoddarhospital.net
Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy.
Your body breaks down most of the food you eat into sugar (glucose) and releases it into your bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. Insulin acts like a key to let the blood sugar into your body cells for use as energy.
With diabetes, your body doesn't make enough insulin or can't use it as well as it should. When there isnt enough insulin or cells stop responding to insulin, too much blood sugar stays in your bloodstream. Over time, that can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease.
There isn't a cure yet for diabetes, but losing weight, eating healthy food, and being active can really help. Other things you can do to help:
There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant).
Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake). This reaction stops your body from making insulin. Approximately 5-10% of the people who have diabetes have type 1. Symptoms of type 1 diabetes often develop quickly. It's usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults. If you have type 1 diabetes, you'll need to take insulin every day to survive. Currently, no one knows how to prevent type 1 diabetes.
With type 2 diabetes, your body doesn't use insulin well and can't keep blood sugar at normal levels. About 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2. It develops over many years and is usually diagnosed in adults (but more and more in children, teens, and young adults). You may not notice any symptoms, so it's important to get your blood sugar tested if you're at risk. Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes, such as:
Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women who have never had diabetes. If you have gestational diabetes, your baby could be at higher risk for health problems. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after your baby is born. However, it increases your risk for type 2 diabetes later in life. Your baby is more likely to have obesity as a child or teen and develop type 2 diabetes later in life.
Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an immune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake). Risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as clear as for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Known risk factors include:
Currently, no one knows how to prevent type 1 diabetes.
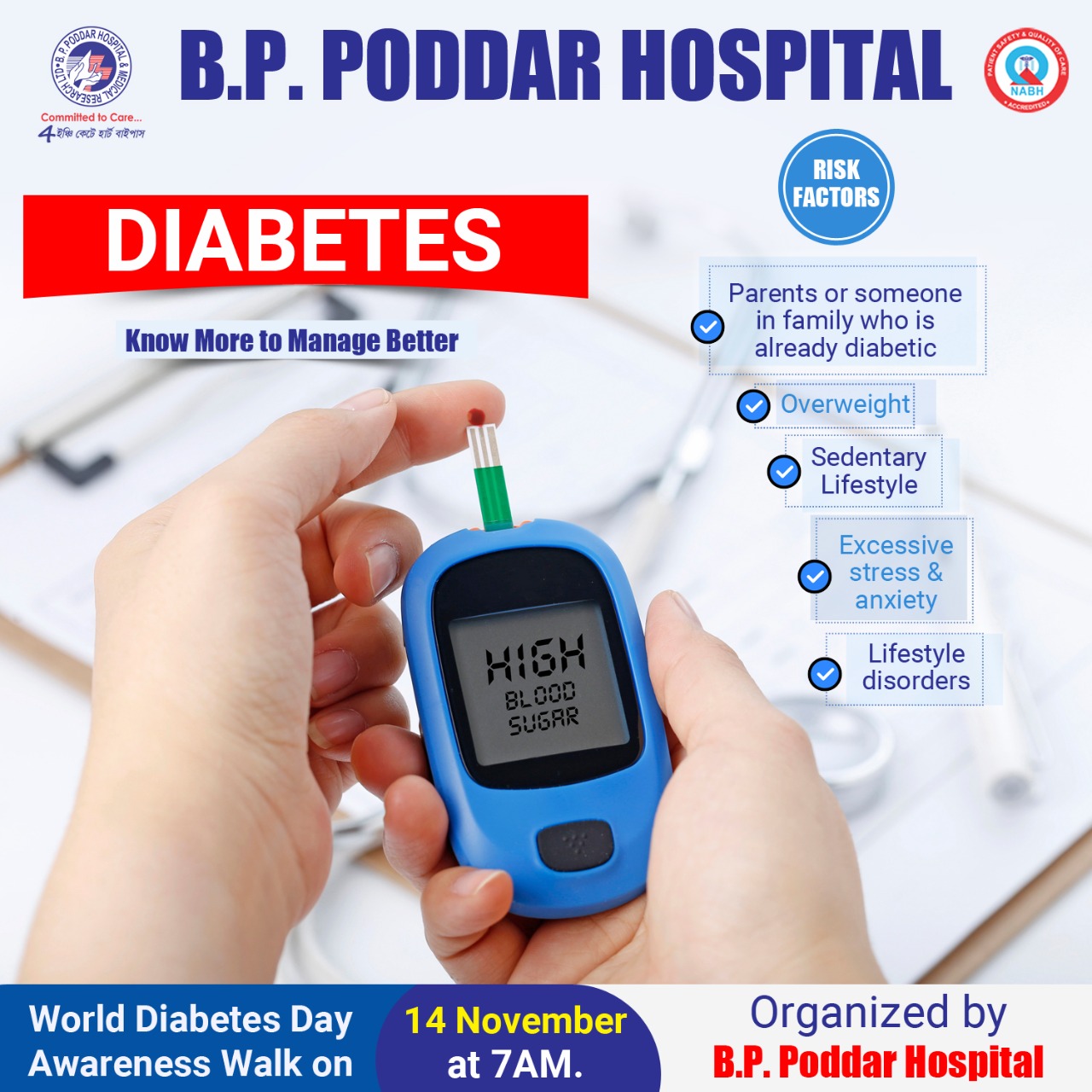
You're at risk for type 2 diabetes if you:
If you have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease you may also be at risk for type 2 diabetes.
You can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes with proven lifestyle changes. These include losing weight if you're overweight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular physical activity.
If you have any of the following diabetes symptoms, see your doctor about getting your blood sugar tested:
People who have type 1 diabetes may also have nausea, vomiting, or stomach pains. Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months and can be severe. Type 1 diabetes usually starts when you're a child, teen, or young adult but can happen at any age.
Type 2 diabetes symptoms often take several years to develop. Some people don't notice any symptoms at all. Type 2 diabetes usually starts when you're an adult, though more and more children and teens are developing it. Because symptoms are hard to spot, it's important to know the risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Make sure to visit your doctor if you have any of them.
Yes! You can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes with proven, achievable lifestyle changes; such as losing a small amount of weight and getting more physically active even if you're at high risk. Read on to find out about lifestyle change program and how you can join.
Before developing type 2 diabetes, most people have prediabetes; their blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough yet for a diabetes diagnosis. Prediabetes is really common. The good news is that prediabetes can be reversed.
Source:
CDC
India Today